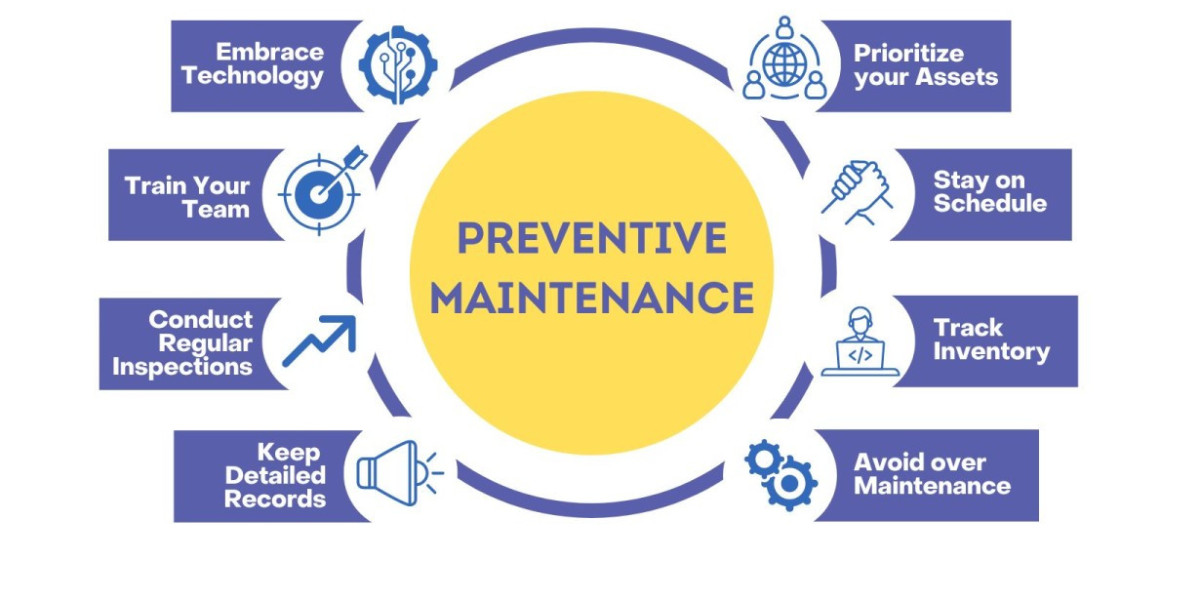
Predictive maintenance (PdM) is an innovative approach that utilizes data analysis, sensor technology, and machine learning to predict equipment failures before they occur. This proactive method helps organizations schedule maintenance activities only when necessary, reducing downtime and operational costs. By continuously monitoring machinery health through IoT sensors, PdM detects early signs of wear and tear, enabling timely interventions. This approach not only extends equipment lifespan but also improves safety and productivity. Implementing predictive maintenance requires integrating various data sources, advanced analytics, and skilled personnel to interpret results accurately. Its effectiveness relies on real-time data collection, predictive algorithms, and maintenance planning aligned with operational needs. As industries adopt PdM, they benefit from minimized unplanned outages, optimized resource utilization, and increased overall equipment efficiency. This strategic shift marks a significant evolution from traditional reactive maintenance methods.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance offers numerous benefits that significantly impact industrial operations. It reduces unexpected equipment failures, which can cause costly downtime and production delays. By predicting issues early, companies can plan maintenance activities during scheduled downtimes, improving overall operational efficiency. PdM also extends the lifespan of machinery by preventing excessive wear and tear through timely interventions. Additionally, it enhances safety by identifying potential hazards before they escalate into accidents. The data-driven approach enables better resource management, optimizing maintenance schedules and inventory. Cost savings are substantial, as preventive repairs are often less expensive than emergency repairs after failure. Overall, predictive maintenance fosters a culture of proactive asset management, leading to higher productivity, lower operational costs, and improved safety standards across industries.
Key Technologies Driving Predictive Maintenance
The success of predictive maintenance depends on a convergence of advanced technologies. IoT sensors are critical, providing real-time data on equipment condition, such as temperature, vibration, and pressure. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to identify patterns indicative of potential failure. Cloud computing platforms facilitate scalable data storage and processing, enabling remote monitoring and analysis. Edge computing allows for on-site data processing, reducing latency and ensuring timely alerts. Additionally, digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets, simulating operational scenarios to predict failures more accurately. Integration of these technologies provides a comprehensive view of asset health, empowering maintenance teams with actionable insights. As technological innovations evolve, predictive maintenance becomes more precise, cost-effective, and accessible for a wide range of industries, transforming traditional maintenance practices into intelligent, data-driven processes.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementing predictive maintenance presents several challenges that organizations must address for successful adoption. Data quality and integration issues can hinder accurate predictions; overcoming this requires standardized data collection protocols and robust IoT infrastructure. High initial investment costs for sensors, software, and training can be a barrier, but long-term savings and efficiency gains justify the expenditure. Resistance to change within organizations may slow adoption; fostering a culture of innovation and providing comprehensive training helps mitigate this. Ensuring cybersecurity of connected devices and data is crucial to prevent breaches. Data overload and false alarms can also complicate decision-making; refining algorithms and setting appropriate thresholds improve reliability. Overcoming these challenges involves strategic planning, stakeholder engagement, and continuous technological upgrades, ultimately leading to more effective and sustainable predictive maintenance programs.
Future Trends in Predictive Maintenance
The future of predictive maintenance is poised for rapid advancement driven by emerging technologies. Artificial intelligence (AI) will enhance predictive accuracy by enabling more sophisticated data analysis and anomaly detection. The integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) will assist technicians with real-time troubleshooting guidance, reducing repair times. Edge computing will become more prevalent, ensuring faster decision-making with minimal latency. Additionally, the adoption of 5G connectivity will facilitate seamless data transfer and real-time monitoring across large industrial sites. Predictive maintenance will increasingly incorporate sustainability metrics, optimizing energy usage and reducing environmental impact. The rise of autonomous maintenance systems, where robots perform routine inspections and repairs, is also anticipated. These trends will make predictive maintenance more accessible, affordable, and efficient, transforming industries into smarter, more resilient ecosystems with minimal downtime and maximum productivity.